As network admins, we often face the grind of manually logging into dozens of switches to pull routine info like VTP configurations. It’s tedious, error-prone, and eats into your day. Enter Python and the Paramiko library: a powerhouse combo for SSH automation that lets you query bulk devices in seconds. In this post, I’ll walk you through a script that connects to a list of Cisco switches, enters enable mode, and extracts the VTP version running on each. We’ll cover setup, code breakdown, and execution—perfect for auditing VLAN propagation across your access layer.
Why Automate VTP Checks?
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) ensures consistent VLAN databases across your Cisco network, but mismatches can lead to outages. Manually running show vtp status on every switch? Not scalable. This script handles it for you, outputting a clean table of IPs and versions. Bonus: It flags legacy VTPv2 as “2<” to highlight upgrade needs.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.x: Grab it from python.org if needed.
- Paramiko: Install via pip: pip install paramiko.
- Device Access: SSH enabled on your switches, with known credentials (username, password, enable password). Test manually first.
- IP List File: A plain text file (e.g., access_switch.txt) with one switch IP per line. Place it in a local folder.
Security Note: Hardcoded creds are for demo only—use environment variables or a secrets manager in production to avoid exposure.
The Script: Step-by-Step
Here’s the full code. Save it as vtp_audit.py. I’ve cleaned up minor quirks from the original (like outdated credential placeholders) for reliability.
python
import paramiko
import sys
import time
import os # For file path checks
# HARDCODED CREDENTIALS - REPLACE WITH YOUR VALUES (USE SECRETS IN PROD)
username = 'your_username' # e.g., 'admin'
password = 'your_password' # e.g., 'cisco123'
enable_password = 'your_enable_password' # e.g., 'enable123'
# Path to TXT file with switch IPs (one per line) - ADJUST FOR YOUR SETUP
ips_file_path = r'C:\path\to\your\access_switch.txt' # Windows example; use / for Linux/Mac
def get_vtp_version(ip, username, password, enable_pass):
"""
SSH into a Cisco switch, enter enable mode, run 'show vtp status', and parse VTP version.
Handles timeouts and errors gracefully.
"""
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
# Connect via SSH
client.connect(
hostname=ip,
username=username,
password=password,
timeout=10,
look_for_keys=False,
allow_agent=False
)
# Invoke interactive shell
shell = client.invoke_shell()
time.sleep(2) # Stabilize prompt
# Enter enable mode
shell.send('enable\n')
time.sleep(1)
output = ''
while not shell.recv_ready():
time.sleep(0.1)
output += shell.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
# Send enable password
shell.send(enable_pass + '\n')
time.sleep(1)
while not shell.recv_ready():
time.sleep(0.1)
output += shell.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
# Run show command
shell.send('show vtp status\n')
time.sleep(3) # Let it process
# Capture full output
while shell.recv_ready():
output += shell.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
time.sleep(0.1)
time.sleep(1) # Drain buffer
while shell.recv_ready():
output += shell.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
# Clean exit
shell.send('exit\n')
time.sleep(1)
client.close()
# Parse VTP version
vtp_version = None
for line in output.split('\n'):
if 'VTP version running' in line:
parts = line.split(':', 1)
if len(parts) > 1:
vtp_version = parts[1].strip()
break
# Flag VTPv2 for awareness
if vtp_version == "2":
vtp_version = "2<"
return vtp_version if vtp_version else "Not found"
except paramiko.AuthenticationException:
print(f"Auth failed on {ip} - check creds.")
return None
except paramiko.SSHException as e:
print(f"SSH issue on {ip}: {e}")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error on {ip}: {e}")
return None
finally:
try:
client.close()
except:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Validate file
if not os.path.exists(ips_file_path):
print(f"ERROR: IP file missing: {ips_file_path}")
sys.exit(1)
# Load IPs
with open(ips_file_path, 'r') as f:
switch_ips = [line.strip() for line in f if line.strip()]
if not switch_ips:
print("ERROR: No IPs in file - add one per line.")
sys.exit(1)
# Cred check (basic safeguard)
if username == 'your_username' or password == 'your_password' or enable_password == 'your_enable_password':
print("ERROR: Update credentials in script (lines 8-10).")
sys.exit(1)
print(f"Loaded {len(switch_ips)} switches from {ips_file_path}")
print("\nFetching VTP versions...\n")
print("Switch IP\t\tVTP Version")
print("-" * 40)
for ip in switch_ips:
version = get_vtp_version(ip, username, password, enable_password)
print(f"{ip}\t\t\t{version}")
print("\nAudit complete. Review for VTPv2 flags.")Code Breakdown
- Imports & Config: Pull in Paramiko for SSH, plus basics like time for delays and os for file checks. Hardcode creds and file path at the top—easy to tweak.
- Core Function (get_vtp_version):
- Connection: Establishes SSH with timeout and auto-accepts host keys (fine for internal nets; lock it down otherwise).
- Interactive Shell: Uses invoke_shell() for command-by-command interaction—key for enable mode, which prompts for passwords.
- Command Flow: Sends enable, creds, then show vtp status. Buffers output with recv_ready() loops to catch everything.
- Parsing: Scans for “VTP version running” line, extracts the value, and tweaks VTPv2 to “2<” for quick spotting.
- Error Handling: Catches auth/SSH fails, logs them, and ensures cleanup.
- Main Block: Loads IPs from your TXT file, validates basics, then loops through queries. Outputs a simple table.
Running the Script
- Update the script: Swap in your creds and IP file path.
- Create access_switch.txt (e.g., in Notepad):
192.168.1.10192.168.1.1110.0.0.5
- Fire it up: python vtp_audit.py.
- Sample Output:
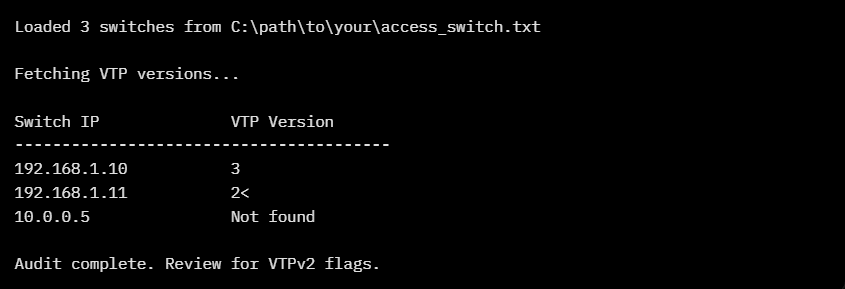
Pro Tips
- Scale It: For 100+ switches, add threading (e.g., via concurrent.futures) to parallelize connections—watch for session limits on your AAA server.
- Enhance Parsing: Tweak the loop for more fields like domain name or mode.
- Logging: Pipe output to CSV with pandas for reports: Add import pandas as pd and df.to_csv(‘vtp_report.csv’).
- Edge Cases: Test on a mix of IOS versions; some older switches might need extra delays.
- Security First: Run from a bastion host, rotate creds post-audit, and never commit secrets to Git.
This script’s a solid starting point for Paramiko-powered automation—adapt it for show run snippets or interface stats next. Got tweaks or war stories? Drop a comment below. Stay scripted, folks.